language
In today’s technology-driven world, a stable and reliable power supply is essential for everything from home electronics to critical business infrastructure. Unfortunately, power interruptions—ranging from momentary voltage drops to extended outages—can occur at any time and often without warning. To safeguard valuable equipment and ensure continuity, many turn to UPS power systems. But what exactly is UPS power, and why is it so important?
This article explains the fundamentals of UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) systems, how they work, and why they play a crucial role in both residential and commercial settings.
What Is UPS Power?
UPS stands for Uninterruptible Power Supply. It is a device that provides emergency backup electricity to connected equipment when the primary power source fails. Unlike generators, which take time to activate, a UPS delivers power instantly—typically in milliseconds—ensuring continuous operation without disruption.
UPS systems contain internal batteries or energy storage systems that kick in when a power issue is detected. In addition to power outages, they also protect against voltage sags, surges, frequency variations, and electrical noise—collectively known as power disturbances.
Why UPS Power Matters
1. Prevents Data Loss and Equipment Damage
A sudden loss of power can cause computers and servers to shut down abruptly, leading to unsaved data being lost or corrupted. For businesses, this could mean the loss of critical documents, transaction records, or customer information. A UPS gives users time to save work and shut down equipment properly.
2. Protects Against Voltage Irregularities
Power from the grid isn’t always clean. Surges, spikes, and brownouts can shorten the lifespan of sensitive electronics or cause immediate failure. A UPS system helps regulate and filter the power, providing a steady, clean output to connected devices.
3. Ensures Continuity for Critical Systems
Whether it’s a medical device, a security system, or an e-commerce platform, many systems must operate without interruption. UPS power ensures continuity for these mission-critical operations, helping to maintain safety, security, and business continuity.
4. Supports Remote and Hybrid Work Environments
In homes and small offices, a UPS can keep internet modems, routers, and computers online during outages, enabling remote workers to continue without interruption.
Types of UPS Systems
There are three main types of UPS systems, each designed for different levels of protection:
1. Offline/Standby UPS
Provides basic protection.
Switches to battery when power fails.
Suitable for home electronics and basic setups.
2. Line-Interactive UPS
Regulates voltage and provides surge protection.
Ideal for small offices or workstations.
3. Online/Double-Conversion UPS
Delivers the highest level of protection.
Continuously powers devices through its inverter, isolating them from all power disturbances.
Commonly used in data centers, hospitals, and industrial environments.
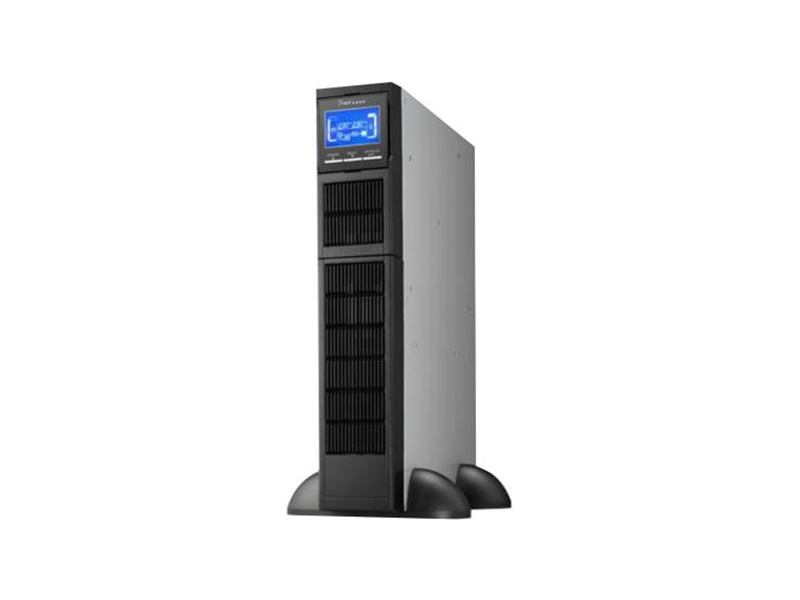
For example, the AF900R series online transformerless rack-mount UPS has single-phase input and single-phase output, complete detection and protection functions, small size, light weight and high working efficiency.

Where UPS Power Is Used
Homes: For computers, routers, smart TVs, and home automation systems.
Offices: For servers, networking equipment, and point-of-sale terminals.
Medical Facilities: For life-saving diagnostic and monitoring devices.
Industrial Settings: For automated machinery and control systems.
Data Centers: To protect critical infrastructure and maintain uptime.
UPS power is more than just a backup plan—it’s a proactive solution to protect your electronics, preserve your data, and maintain operations during power disruptions. Whether you're managing a home office or a mission-critical facility, investing in a UPS system is a smart and necessary step toward ensuring stability, safety, and reliability.